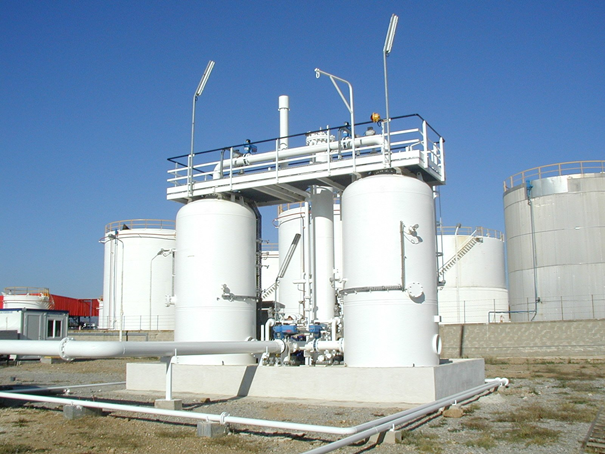

Activated Carbon VRU – dry vacuum pump
Process Description
The hydrocarbon vapour recovery system is based on the well-known process of adsorption on activated carbon. The saturated carbon is regenerated by means of vacuum. The hydrocarbons desorbed from the carbon are re-absorbed in one of the products present on the storage terminal. An adsorption process is not continuous and needs to be stopped after a while to allow regeneration of the carbon. To ensure free passage of vapours through the system at all times, at least two carbon beds are required. The opening and closing of the sequential valves is such that one bed is always on line.
Whilst a tank truck is filled with a product or more products simultaneously, the mixture of air and hydrocarbon vapours is forced out of the compartments and is led through a common pipe to a 4” API vapour coupler, located in the same area as the product loading points. From there the vapours run through a vapour arm or hose with detonation arrestor to a common vapour collecting line. The vapour collector is connected to the VRU.
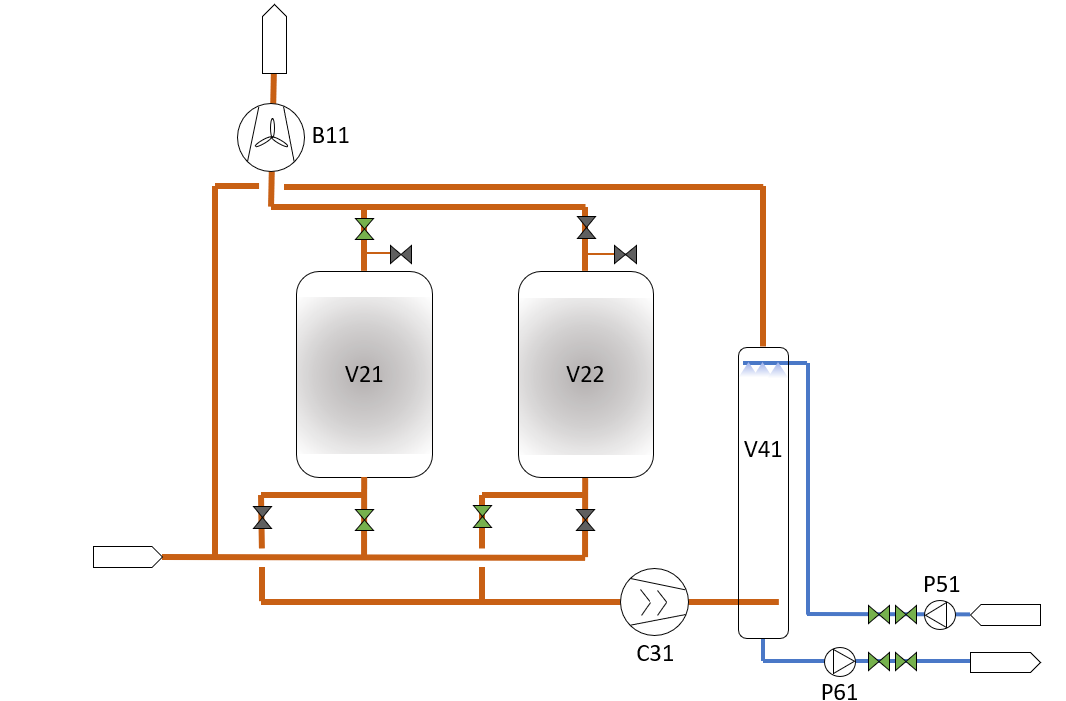
The hydrocarbon/air mixture usually flows upwards through the carbon beds. The hydrocarbons are rapidly adsorbed in the pores of the activated carbon in the bottom of the bed. The mid section of the bed functions as a buffer to balance out fluctuations in flow rate and concentration. The top of the bed functions as purification section to obtain the required emission level.
The regeneration of the activated carbon is done by pulling vacuum by means of dry screw vacuum pumps. The engineers have developed this technology specially to overcome the problems of corrosion and abrasion related to the use of glycol based seal liquid in liquid ring vacuum pumps. On top of that, the dry pumps consume approximately 40% less energy. Because the dry screw pumps can be equipped with frequency controllers, the capacity of the pump can be perfectly adapted to the fluctuating needs in a vapour recovery system.
This way a secondary means is available to reduce the overall energy consumption considerably. The load of hydrocarbons on the activated carbon is also more balanced, which reduces the risk of hot spots.
Gasoline and diesel vapours consist mainly of butane and pentane. Their re- absorption in one of the products of the terminal will slightly increase the REID Vapour Pressure (RVP) of the product. It is therefore recommended the use of product with a reasonable daily throughput as absorbent for the VRU.
The re-absorber is a simple wash tower. The highly concentrated hydrocarbons coming from the vacuum system are brought in direct contact with the absorbent in counter flow on a packed bed of Raschig Super Rings. The rest of the air, saturated with the new hydrocarbons from the absorbent, leaves the column from the top and is led back to the inlet of the VRU.
If you have any question, please submit the form below!

